Hambone - Mrxbox98
Description
I hid the flag somewhere on the website as a 48 byte hex value, so I know you’ll never find it. Just, don’t check out how the background is calculated.
https://hambone.chall.pwnoh.io
Note: the flag will be in lowercase, not uppercase
File: dist.py
def get_distances(padded_url : str, flag_path : str):
distances = []
for i in range(3):
# calculate hamming distance on 16 byte subgroups
flag_subgroup = flag_path[i*32:i*32+32]
z = int(padded_url[i*32:i*32+32], 16)^int(flag_subgroup, 16)
distances.append(bin(z).count('1'))
return distances
Solution
Here is an annotated version of the code.
# Calculates the distance for the website background
# @param padded_url: The path in the request url; 96 length hexadecimal string
# @param flag_path: The path to get the flag; 96 length hexadecimal string
def get_distances(padded_url : str, flag_path : str):
distances = [] # The distances for the background
for i in range(3): # RGB Triplet
# calculate hamming distance on 16 byte subgroups
flag_subgroup = flag_path[i*32:i*32+32] # Gets 32 chars of the string based on which iteration it is on
z = int(padded_url[i*32:i*32+32], 16)^int(flag_subgroup, 16) # Gets the bit difference between the current 32 hex section and the flag 32 hex section
distances.append(bin(z).count('1')) # Adds the number of 1's to the distance
return distances # Returns the distance array
The path for the flag url and the solution url should be in this format
32 chars 32 chars 32 chars
╭──────────────────────────────╮ ╭──────────────────────────────╮ ╭──────────────────────────────╮
ac72c3ecbd95984a48a1890735da8c10 b7dd222b9addf2ab7b17778c6b8fc353 7852861c969f6738865996481438b29d
The path’s binary length is 384 and since the binary is being compared, the first step is to use binary then convert to hex before testing the string.
The python operator ^ compares the binary of two integers.
This is the exploit we can use to guess and check bits in our path.
Here is an example:
11000
01011
───── XOR Operator
10011
If the two bits are the same the binary of the background will have a 0 in that place and if they are different the binary will have a 1. Since the background is calculated based off of how many 1’s are in the binary difference, we can first check the background for all 0s then change each bit one by one and observing the change that occurs in the background. If the background hex increased, that means the bit we changed was wrong, if the background hex value decreases that means that the bit we changed was correct.
Example:
Zero path: 000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Correct path: ac72c3ecbd95984a48a1890735da8c10b7dd222b9addf2ab7b17778c6b8fc3537852861c969f6738865996481438b29d
Binary:
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011101
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011101
Example:
Zero path: 000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Correct path: ac72c3ecbd95984a48a1890735da8c10b7dd222b9addf2ab7b17778c6b8fc3537852861c969f6738865996481438b29d
Binary:
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011101
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011101
Number of 1s: 190:
000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011101
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011100
Number of 1s: 189
By testing each of the 384 bits one by one, we can find the value of each bit by checking if the number of 0s decreases or increases. Here is a small helper function to test our solutions using the python requests package:
def get_background(path : str):
req = requests.get(f"https://hambone.chall.pwnoh.io/{path}")
background = req.text.split("background: #")[1].split("\"")[0]
return int(background, 16)
Here is the final solution:
import requests
# Calculates the distance for the website background
# @param padded_url: The path in the request url; 96 length hexadecimal string
# @param flag_path: The path to get the flag; 96 length hexadecimal string
def get_distances(padded_url : str, flag_path : str):
distances = [] # The distances for the background
for i in range(3): # RGB Triplet
# calculate hamming distance on 16 byte subgroups
flag_subgroup = flag_path[i*32:i*32+32] # Gets 32 chars of the string based on which iteration it is on
z = int(padded_url[i*32:i*32+32], 16)^int(flag_subgroup, 16) # Gets the bit difference between the current 32 hex section and the flag 32 hex section
distances.append(bin(z).count('1')) # Adds the number of 1's to the distance
return distances # Returns the distance array
def get_background(path : str):
req = requests.get(f"https://hambone.chall.pwnoh.io/{path}")
background = req.text.split("background: #")[1].split("\"")[0]
return int(background, 16)
# The background when the value of the path is 0
zero_bg = "c6b4c5"
curr_path = ""
for i in range(384):
path = "0"*(383-i)+"1"+"0"*i
dis = hex(int(path, 2)).split("0x")[1].zfill(96)
print(f"Currently testing: {dis}")
result = get_background(dis)
zero = int(zero_bg, 16)
current = result
if current > zero:
curr_path = "1"+curr_path
else:
curr_path = "0"+curr_path
print(curr_path)
Output:
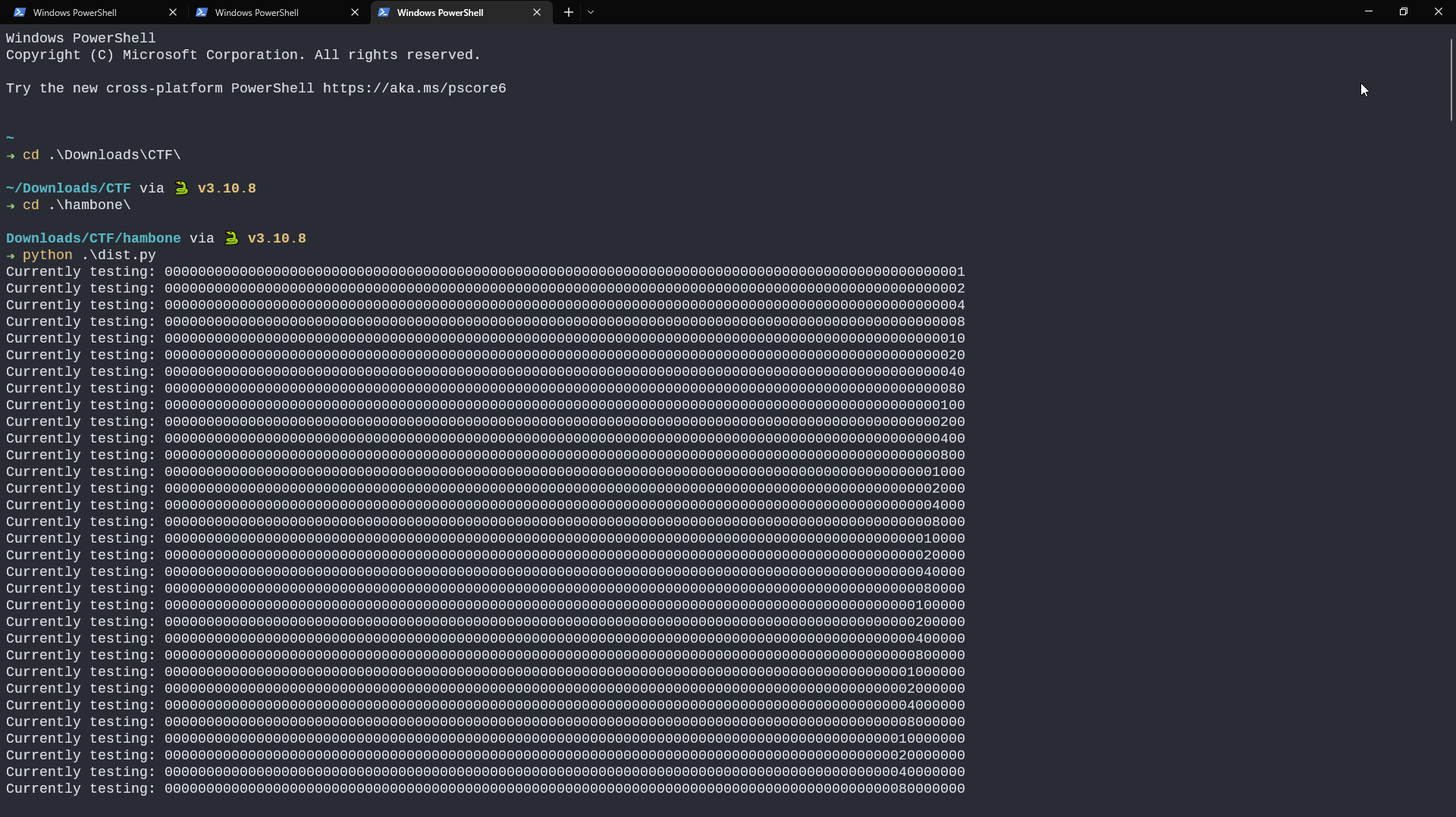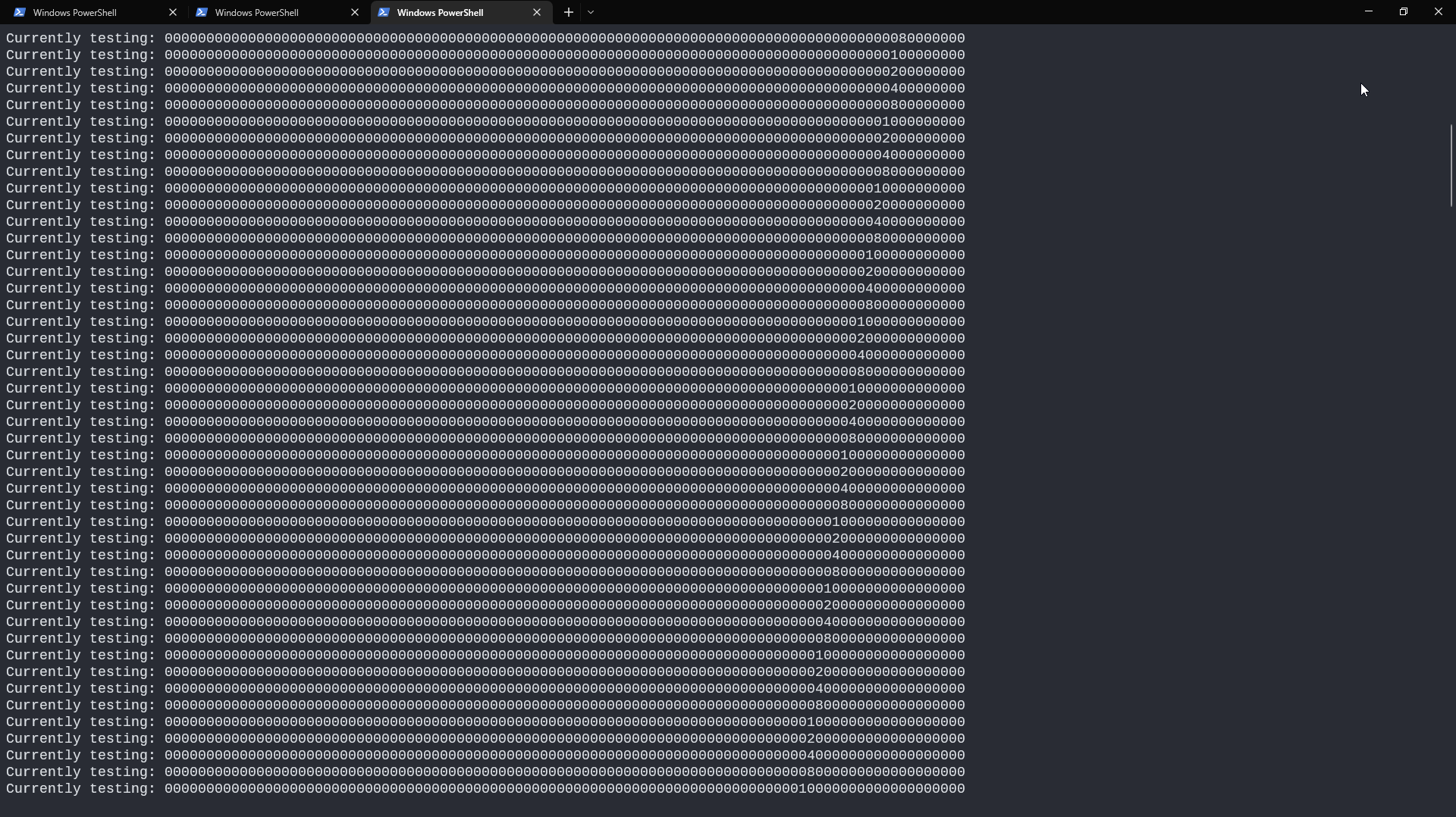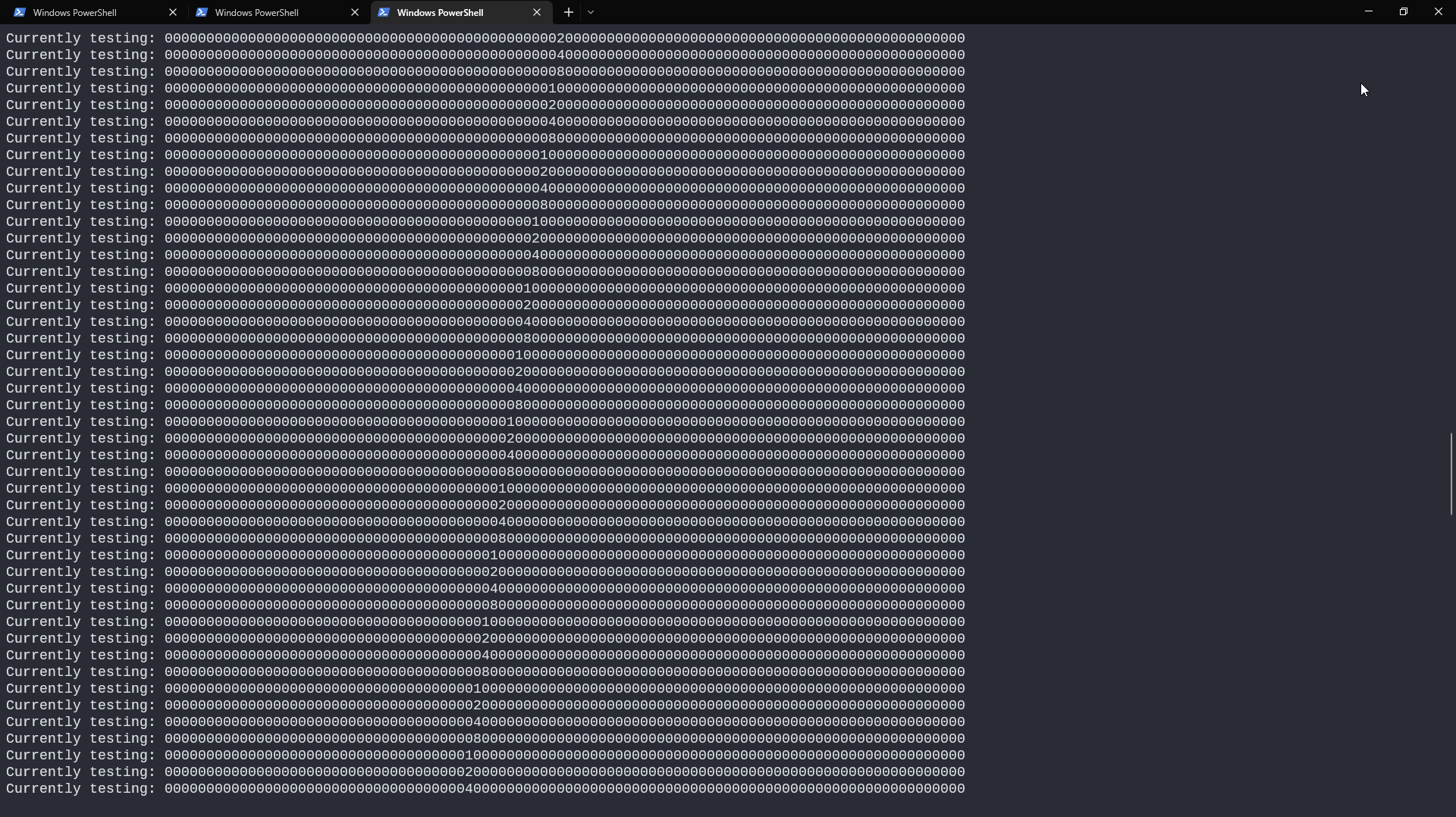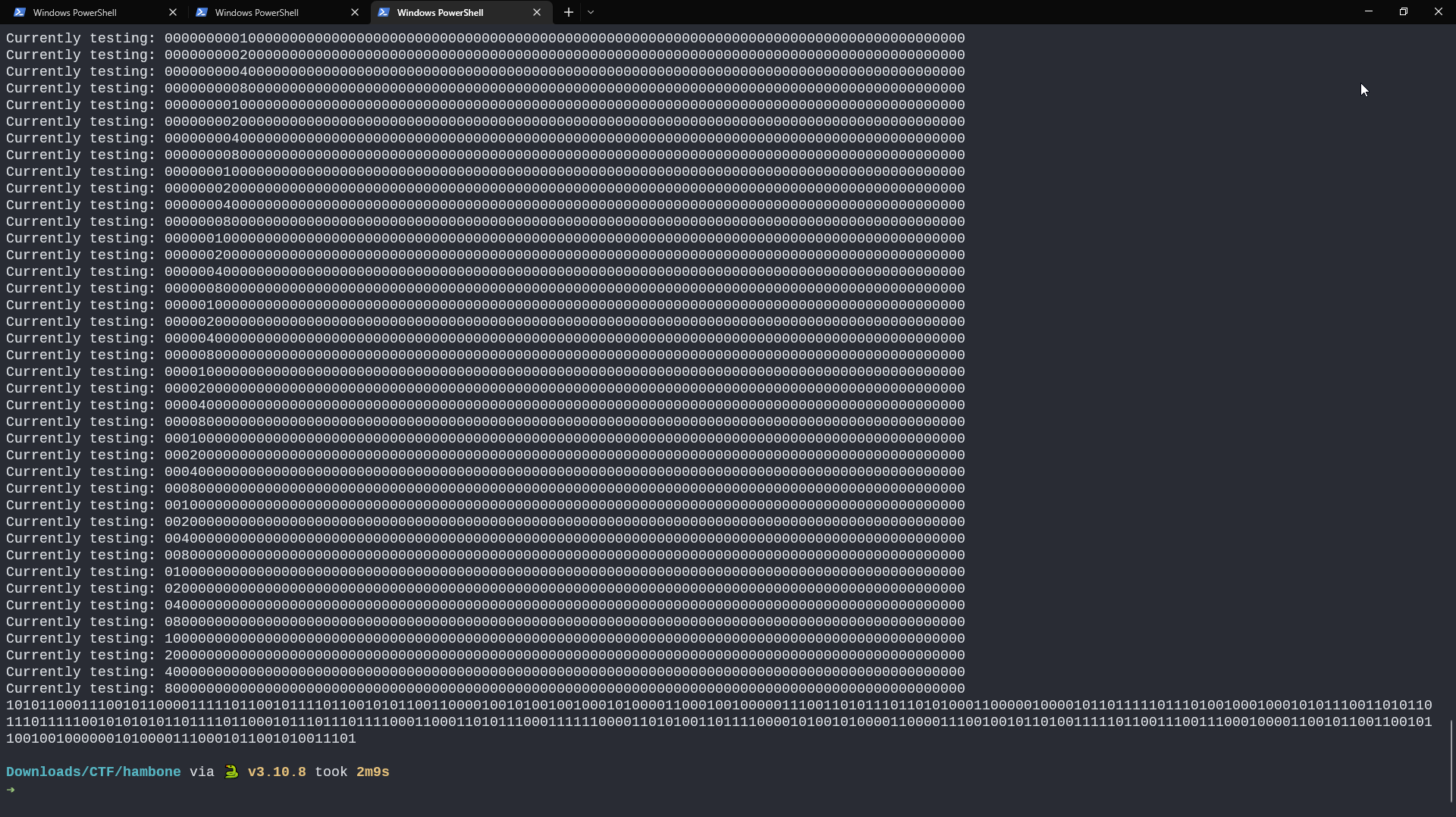
At the end the program will output
101011000111001011000011111011001011110110010101100110000100101001001000101000011000100100000111001101011101101010001100000100001011011111011101001000100010101110011010110111011111001010101011011110110001011101110111100011000110101110001111110000110101001101111000010100101000011000011100100101101001111101100111001110001000011001011001100101100100100000010100001110001011001010011101
which converted into hex is
ac72c3ecbd95984a48a1890735da8c10b7dd222b9addf2ab7b17778c6b8fc3537852861c969f6738865996481438b29d
which means the final path is this Chrome and some other browsers sometimes autocapitalize the path, but running
wget https://hambone.chall.pwnoh.io/ac72c3ecbd95984a48a1890735da8c10b7dd222b9addf2ab7b17778c6b8fc3537852861c969f6738865996481438b29d
creates a file with the contents:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.2.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha384-OERcA2EqjJCMA+/3y+gxIOqMEjwtxJY7qPCqsdltbNJuaOe923+mo//f6V8Qbsw3" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.2.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-Zenh87qX5JnK2Jl0vWa8Ck2rdkQ2Bzep5IDxbcnCeuOxjzrPF/et3URy9Bv1WTRi" crossorigin="anonymous">
<title></title>
</head>
<body style="background: #ffffff">
<div id="content">
<div class='container-fluid my-5'>
<p style="color:#000000"> Whoa! How'd you find this? Guess I owe you the flag: buckeye{th3_b4ckgr0und_i5_n0t_4_l13} </p>
</div>
</div>
<div>
</body>
</html>
so the flag is buckeye{th3_b4ckgr0und_i5_n0t_4_l13}
Bonce - null
Description
nonce without a cipher
Given an encrypted message and a known stream cipher-esque encryption function, find the flag in the message.
File: bonce.py
import random
with open('sample.txt') as file:
line = file.read()
with open('flag.txt') as file:
flag = file.read()
samples = [line[i:i+28] for i in range(0, len(line) - 1 - 28, 28)]
samples.insert(random.randint(0, len(samples) - 1), flag)
i = 0
while len(samples) < 40:
samples.append(samples[len(samples) - i - 2])
i = random.randint(0, len(samples) - 1)
encrypted = []
for i in range(len(samples)):
x = samples[i]
if i < 10:
nonce = str(i) * 28
else:
nonce = str(i) * 14
encrypted.append(''.join(str(ord(a) ^ ord(b)) + ' ' for a,b in zip(x, nonce)))
with open('output.txt', 'w') as file:
for i in range(0, 4):
file.write('input: ' + samples[i] + '\noutput: ' + encrypted[i] + '\n')
file.write('\n')
for i in range(4, len(samples)):
file.write('\ninput: ???\n' + 'output: ' + encrypted[i])
File output.txt
input: Look in thy glass, and tell
output: 124 95 95 91 16 89 94 16 68 88 73 16 87 92 81 67 67 28 16 81 94 84 16 68 85 92 92 16
input: the face thou viewestNow is
output: 69 89 84 17 87 80 82 84 17 69 89 94 68 17 71 88 84 70 84 66 69 127 94 70 17 88 66 17
input: the time that face should fo
output: 70 90 87 18 70 91 95 87 18 70 90 83 70 18 84 83 81 87 18 65 90 93 71 94 86 18 84 93
input: rm another;Whose fresh repai
output: 65 94 19 82 93 92 71 91 86 65 8 100 91 92 64 86 19 85 65 86 64 91 19 65 86 67 82 90
input: ???
output: 70 20 93 82 20 90 91 67 20 64 92 91 65 20 90 91 64 20 70 81 90 81 67 81 71 64 24 96
input: ???
output: 93 90 64 21 81 90 70 65 21 87 80 82 64 92 89 80 21 65 93 80 21 66 90 71 89 81 25 21
input: ???
output: 67 88 84 90 83 69 69 22 69 89 91 83 22 91 89 66 94 83 68 24 112 89 68 22 65 94 83 68
input: ???
output: 82 23 94 68 23 68 95 82 23 68 88 23 81 86 94 69 23 64 95 88 68 82 23 66 89 82 86 69
input: ???
output: 218 8340 8474 92 24 79 87 85 90 124 81 75 92 89 81 86 75 24 76 80 93 24 76 81 84 84 89 95
input: ???
output: 92 25 86 95 25 77 81 64 25 81 76 74 91 88 87 93 75 64 6 118 75 25 78 81 86 25 80 74
input: ???
output: 17 88 84 16 66 95 17 86 94 94 85 16 70 89 93 92 17 82 84 16 69 88 84 16 69 95 92 82
input: ???
output: 126 87 17 89 88 66 17 66 84 93 87 28 93 94 71 84 29 17 69 94 17 66 69 94 65 17 65 94
input: ???
output: 66 70 84 64 88 70 72 13 101 90 94 71 17 83 67 70 17 70 89 75 17 95 94 70 89 87 67 208
input: ???
output: 8349 8465 66 19 86 95 80 64 66 31 17 82 95 87 17 64 89 86 17 90 95 19 69 91 84 86 114 82
input: ???
output: 93 88 66 20 83 85 82 95 17 64 89 81 17 88 94 66 84 88 72 20 112 68 67 93 93 20 94 82
input: ???
output: 17 93 84 71 17 69 67 92 92 80 11 102 94 21 69 93 94 64 17 65 89 71 94 64 86 93 17 66
input: ???
output: 88 88 85 89 70 69 17 89 87 22 69 94 88 88 84 22 80 81 84 22 66 94 80 90 93 22 66 83
input: ???
output: 84 115 84 68 65 94 69 82 17 88 87 23 70 69 88 89 90 91 84 68 17 67 89 94 66 23 69 95
input: ???
output: 72 24 86 87 93 92 84 86 17 76 88 85 84 22 115 77 69 24 88 94 17 76 89 87 68 24 93 81
input: ???
output: 83 76 82 82 84 64 84 66 66 86 92 92 110 74 80 64 110 74 94 84 84 95 88 74 89 3 24 68
input: ???
output: 68 85 30 16 64 85 95 85 95 82 87 66 208 8348 8464 84 18 94 93 68 18 68 93 16 80 85 30 116
input: ???
output: 91 84 18 66 91 95 85 93 87 29 18 80 92 85 18 69 90 88 92 84 18 88 95 80 85 84 18 85
input: ???
output: 68 87 30 18 64 87 95 87 95 80 87 64 208 8350 8464 86 18 92 93 70 18 70 93 18 80 87 30 118
input: ???
output: 64 19 91 85 18 93 93 68 18 71 90 92 71 19 92 92 70 19 64 86 92 86 69 86 65 71 30 103
input: ???
output: 126 91 93 95 18 93 92 20 70 92 75 20 85 88 83 71 65 24 18 85 92 80 18 64 87 88 94 20
input: ???
output: 65 65 87 71 91 65 75 10 102 93 93 64 18 84 64 65 18 65 90 76 18 88 93 65 90 80 64 215
input: ???
output: 71 88 80 90 87 69 65 22 65 89 95 83 18 91 93 66 90 83 64 24 116 89 64 22 69 94 87 68
input: ???
output: 87 23 91 68 18 68 90 82 18 68 93 23 84 86 91 69 18 64 90 88 65 82 18 66 92 82 83 69
input: ???
output: 64 85 18 89 92 87 70 80 87 74 9 111 90 87 65 93 18 94 64 93 65 80 18 74 87 72 83 81
input: ???
output: 68 92 30 25 64 92 95 92 95 91 87 75 208 8341 8464 93 18 87 93 77 18 77 93 25 80 92 30 125
input: ???
output: 65 16 90 86 19 94 92 71 19 68 91 95 70 16 93 95 71 16 65 85 93 85 68 85 64 68 31 100
input: ???
output: 65 92 19 80 93 94 71 89 86 67 8 102 91 94 64 84 19 87 65 84 64 89 19 67 86 65 82 88
input: ???
output: 86 18 92 84 19 70 91 75 19 90 70 65 81 83 93 86 65 75 12 125 65 18 68 90 92 18 90 65
input: ???
output: 86 19 90 64 19 64 91 86 19 64 92 19 85 82 90 65 19 68 91 92 64 86 19 70 93 86 82 65
input: ???
output: 86 20 92 82 19 64 91 77 19 92 70 71 81 85 93 80 65 77 12 123 65 20 68 92 92 20 90 71
input: ???
output: 95 89 64 21 81 84 80 94 19 65 91 80 19 89 92 67 86 89 74 21 114 69 65 92 95 21 92 83
input: ???
output: 86 22 92 80 19 66 91 79 19 94 70 69 81 87 93 82 65 79 12 121 65 22 68 94 92 22 90 69
input: ???
output: 69 82 31 23 65 82 94 82 94 85 86 69 209 8347 8465 83 19 89 92 67 19 67 92 23 81 82 31 115
input: ???
output: 8351 8474 64 24 84 84 82 75 64 20 19 89 93 92 19 75 91 93 19 81 93 24 71 80 86 93 112 89
input: ???
output: 65 84 19 88 93 86 71 81 86 75 8 110 91 86 64 92 19 95 65 92 64 81 19 75 86 73 82 80
Encryption Theory
The nonce for each output is given by the bonce.py script. Each nonce is a 28 character string. The nonce is the index of the output repeated until it reaches 28 characters. For example, the nonce for output 0 is 0000000000000000000000000000 and the nonce for output 10 is 1010101010101010101010101010.
The encryption process begins by splitting the input string into 28 character segments, and then inputting a 28 character flag randomly between the segments. Then, the input is padded into 40 segments by randomly repeating input phrases. Each segment is encrypted by XORing the Unicode encoding of each segment with the nonce of it’s index. For the example of the zero-th segment, this means that the input string Look in thy glass, and tell is converted to Unicode, 76 111 111 107 32 105 110 32 116 104 121 32 103 108 97 115 115 44 32 97 110 100 32 116 101 108 108 32, and then XORed with 0000000000000000000000000000, which gives the output, 124 95 95 91 16 89 94 16 68 88 73 16 87 92 81 67 67 28 16 81 94 84 16 68 85 92 92 16.
Solution Theory
Since the nonce is known for each output, it is possible to reverse engineer the initial plaintext. The XOR functions like a negative sign; (A XOR B) XOR B = A. Therefore, XORing the encrypted output with the known nonce will give back the plaintext.
Solution
# First, generate the string of nonces. Each character of the nonce will be XORed with a character of the ciphertext
nonces = ""
for i in range(10):
nonces = nonces + 28 * str(i)
for i in range(10,40):
nonces = nonces + 14 * str(i)
# Second, read and parse the output cipher texts from the output.txt file
outputs = []
puts = []
with open("output.txt", "r") as a:
out = a.read()
o = out.split("\n")
for i in o:
if i.find("input") == -1:
puts.append(i)
for i in range(len(puts)):
puts[i] = puts[i][8:]
for i in puts:
outputs.extend(i.split(" "))
while True:
try:
outputs.remove(" ")
except:
break
while True:
try:
outputs.remove("")
except:
break
# Third, decipher the message by XORing each cipher character with each nonce character
message = []
for i, j in zip(outputs, nonces):
message.append(int(i) ^ ord(j))
# Fourth, generate a string containing the entire plaintext
m = ""
for i in message:
m = m + chr(i)
# Fifth, print the entire plaintext and the flag
print(m)
print(m[m.find("buckeye"):m.find("buckeye")+28])
The final flag is found to be buckeye{some_say_somefish:)} The plaintext is taken from William Shakespeare’s Sonnet 3.